Respiratory diseases affect the organs and tissues of the respiratory system, which is responsible for oxygenating the blood and removing carbon dioxide from the body. This system comprises the upper and lower respiratory tracts, as well as the paired respiratory organs, the lungs. The upper part includes the nasal cavity and nasopharynx, while the lower part consists of the larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs. Pulmonology is the branch of medicine that focuses on the study of respiratory diseases. Pulmonologists specialize in diagnosing, treating, and preventing lung and bronchial pathologies. These diseases can often be severe, require long-term treatment, and lead to serious consequences. To prevent a decline in quality of life and life expectancy, it is crucial to begin treatment as early as possible.
Main symptoms
The main symptoms of respiratory system disease include:
- a persistent sore throat, prolonged dry cough or cough with phlegm;
- shortness of breath, which appears even after minor physical activity;
- pain in the chest area;
- elevated body temperature for a long period of time;
- breathing problems, inability to breathe fully;
- increased snoring.
Causes of diseases
The prevalence of respiratory pathologies is influenced by many factors. The main causes of the occurrence and development of diseases are:
- infections – viruses, parasites, bacteria;
- unfavorable climatic conditions – cold, damp or too dry air;
- polluted atmosphere – exhaust gases, industrial emissions;
- allergens – food products, pollen of flowering plants, animal hair, household dust;
- hereditary predisposition to pathologies;
- low immunity, autoimmune diseases;
- smoking, poor nutrition;
- oncology of the lungs and bronchi.
To establish the cause will help the doctor. He will conduct an examination and prescribe the necessary procedures.
Prevention of respiratory diseases
- Walking in the fresh air
Walking is the key to respiratory health. During a walk, we breathe more often, actively working lungs. Thanks to which the blood is saturated with oxygen. This allows all other systems to receive more nutrients with the blood flow. In addition, toxins and harmful substances are removed from the tissues faster. In addition to walking, frequent airing of the room is necessary, as well as damp cleaning.
- Passive (natural) inhalation
Passive inhalation is the inhalation of warm vapors saturated with easily evaporated essential oils or decoctions of herbs, which have a disinfecting, anti-inflammatory effect on the respiratory tract. Passive inhalation is most often used to prevent influenza and acute respiratory viral infections, as it disinfects the respiratory tract and the air a person breathes.
- Correct breathing
Correct and natural breathing is breathing through the nose, passing through its cavity air enters the nasopharynx, where it becomes cleaner and warmer. The mucous membrane of the nasal cavity with cilia prevents the penetration of harmful microorganisms and dust into the respiratory tract.
- Breathing exercises
As a preventive measure against respiratory diseases, it is desirable to do daily breathing exercises. When performing exercises develops respiratory muscles, speech apparatus, there is oxygenation of the blood.

- Healthy lifestyle, motor activity
Full proper nutrition, hardening, smoking cessation – all this contributes to increasing the body’s resistance to infection. Sufficient physical activity – running, swimming, morning exercise – increases the level of carbon dioxide in the body.
- Protection against viruses during epidemics
During epidemics of viral diseases, it is extremely important to avoid large crowds of people as this increases the risk of infection. Mass events, public places and transportation can become sources of infection. To protect yourself, it is recommended to maintain a social distance and wear personal protective equipment, such as masks and gloves, which help reduce the likelihood of exposure to the virus.
- Use of respirators
If you work in a facility that releases harmful substances into the air, it is important to use protective equipment such as respirators to minimize exposure to hazardous chemical or toxic particles. A respirator can help prevent them from entering your respiratory tract and reduce health risks.
- Follow good personal hygiene practices.
Wash your hands after going outdoors and visiting public places.
Environmental influences on respiratory health
The environment has a significant impact on respiratory health. Air pollution, exhaust fumes, chemical emissions, industrial dust, and allergens such as pollen and animal hair can seriously affect lung and bronchial health. Constant exposure to these factors contributes to the development of chronic respiratory diseases such as bronchitis, asthma, and even lung cancer.
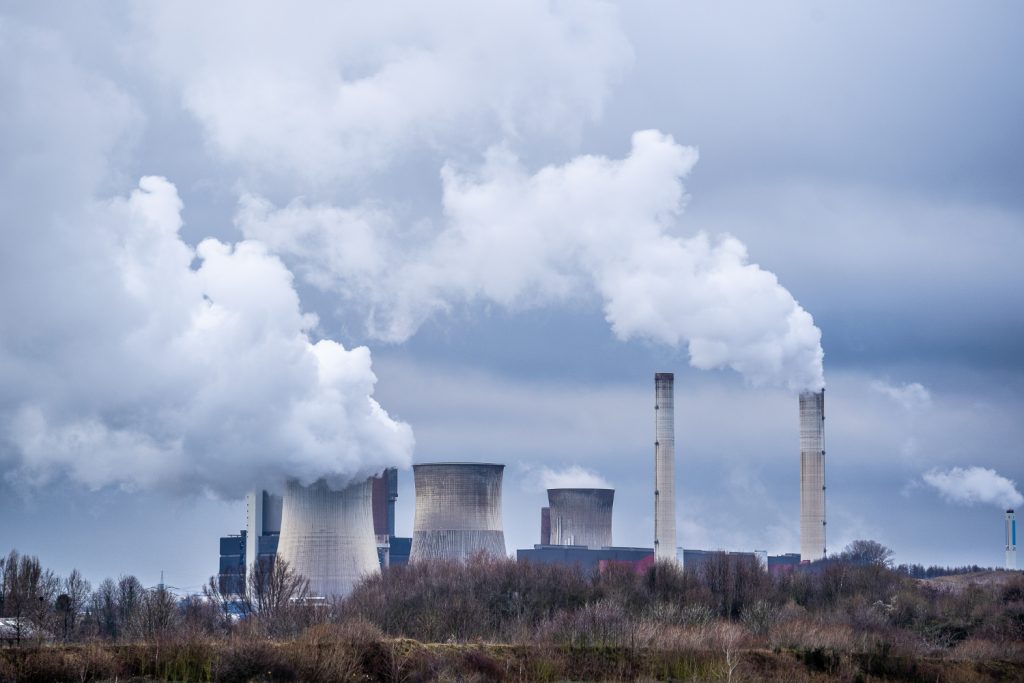

In addition, inhaling polluted air can lead to inflammation in the respiratory tract, impaired oxygen metabolism and increased stress on the cardiovascular system. People living in areas with high levels of pollution are at increased risk of developing chronic respiratory diseases.
To protect your lungs, it’s important to monitor indoor air quality and the places you spend time. Regular ventilation, air purifiers and humidifiers can help reduce the concentration of dust and allergens. You should also avoid spending long periods of time outdoors on high-pollution days, especially for people prone to respiratory problems.
Conclusion
Respiratory diseases require careful attention and timely treatment. Following simple preventive measures such as walking outdoors, proper breathing and regular physical activity will help maintain a healthy respiratory system. It is also important to monitor environmental quality, avoid polluted air, and use protective equipment in unfavorable conditions. Understanding the causes and symptoms of diseases, as well as regular check-ups with specialists, will help to prevent or detect pathologies in time and avoid serious consequences.